 |






|
|
ART - LUINI - VILLA LA PELUCCA - PAGE 2
|
|
|
Esoteric Practices |
Hidden knowledge |
- Esoteric practices are everything you do from a spiritual perspective to help
you grow as a person and develop a deeper knowledge of the universe and
your place within it.
- Esotericism comes from all four corners
of the world, East and West.
|
Ignorance is the curse of God; knowledge is the wing wherewith we fly to heaven.
(Shakespeare)
|
Eastern esotericism
(kind of) |
- There are many Indian esoteric traditions such as Hindu mysticism, connected primarily with Tantrism.
-
Esoteric Buddhism, and Vajrayana (vajra meaning 'diamond' or 'ray'),
concerns the unchanging and indestructible state of awakening and are also used interchangeably.
- Taoism involves communication with spirits, meditation, body movements, medicine, and
'internal alchemy.'
- Confucianism is characterized as a system
of social and ethical philosophy but it was also used to build the
ancient religious foundation in Chinese society.
|
Well, a lot of it was written in ancient
Sanskrit. Things like the archaic Vedic tradition
based on its primal hymns, later Hindu, Tantrik, and
Buddhist spiritual traditions and their many
Guru-disciple lineages, Yoga, the vast fields of
Mantra Shastra (based on Seed Syllables) and Yantra
Shastra, the chakra system, the Kundalini and the
elaborate techniques to manipulate the inner anatomy
of the subtle body, the fivefold breaths, the
incredibly sophisticated Jyotisha system of astrology,
Yogik and Tantrik alchemy, the Tattwas, the Hindu five
element system, herbalism and Ayurveda medicine, the
many different Lokas or worlds, the God- and
Goddess-forms and their vehicles and animals, the
ancient traditions preserved in specific temples, the
old methods of warding off or exorcising demons, and
many other traditions of magic.
(Devala Rees)
|

Western esotericism |
- Depending on the definitions, most Western esotericism could be considered
rooted in Eastern traditions,
despite what some seem to think.
- Although many claim there is
no such thing as Eastern Hermeticim, because it was a combination of
many ancient spiritual systems that were never called Hermeticism,
that's a Western word.
- The earliest traditions of Western esotericism, Hermeticism, Gnosticism and Neoplatonism developed as schools of thought distinct from what became mainstream Christianity
emerged in the Eastern Mediterranean during late antiquity.
|
The terms “esotericism” and “Western esotericism”
were coined in the West, from a Western perspective.
Various academics have posited that esotericism is a
phenomenon or notion unique to the Western world.
There is no clearly comparable category of Eastern
esotericism. One main reason for this is that in the
Western world, the dominant religion (Christianity)
suppressed rival spiritual systems and practices,
forcing them to become hidden, underground, “esoteric”
traditions.
(Devala Rees)
|
Spiritual and
mystical practices |
-
Deeper knowledge includes many aspects encompassing religion,
science, philosophy, mysticism and spirituality.
- The Bible,
which was taken from the Sumerian tablets, is seen as a religious
text but also a magical tool in esoteric practices, not only as a
symbol of faith, but also as a potent talisman.
- The narratives
and parables offer mystical insights, conjuring spells and healing
prayers and intertwine spirituality and practical magic.
- It's
not just about faith in the Divine, but actively engaging with these
spiritual forces to help navigate life.
|
Esoteric is defined as “very unusual and understood or liked by only a small number of people, especially those with special knowledge.” The term “esoteric” comes from the Greek 'esōterikos' and is derived from 'esōterō' meaning “inner” or “further inside.” Thus, the idea of the esoteric is generally associated with secret or hidden knowledge, a theme that can be found throughout history and across cultures.
(Cambridge Dictionary)
|

Alchemy and the
occult |
- In ancient Greece, there was a strong connection between esoteric meaning and the study of philosophy.
-
During the Middle Ages, people associated the esoteric with studying alchemy and the occult
and Alchemists were considered scientists and philosophers.
- By the Renaissance, esoteric knowledge
was associated with spiritual or religious pursuits.
|
Of all knowledge, the wise and good seek mostly to know themselves.
(Shakespeare)
|
Destiny |
- Esoterism is all about actively engaging with the
spiritual realm and receiving spiritual assistance.
- It's a quest for understanding
and connection whether by understanding our place in the universe
through astrology, or uncovering hidden knowledge through numerology
or using rituals and spells to shape personal destiny.
- For
example, the Bible Psalms are used in rituals because their poetic verses
are believed to carry divine energy.
|
Listen to many, speak to a few.
(Shakespeare)
|

Rituals |
- Rituals are a way of opening a dialogue with the
spiritual world and inviting it into our lives.
- They are not
passive acts and require intent, focus and an active participation.
- The practioner is the medium through which spiritual energy is
channeled and these acts are not confined to a specific culture or
religion because they are universal.
- For example, whether it's
lighting a candle in Wicca, or incense in Buddhism, these rituals
serve as a bridge between the physical and spiritual world.

Head float |
- There has been a huge bias that encompasses what are
called esoteric practices, as most of them are spiritual and
mystical ideals considered evil (by some) because they operate
outside of the Abrahamic religions, although this is not always the
case.
- An example of this bias is the word 'pagan' which is
what Christians called anyone who believed in pre-Christian
traditions, in other words, all their ancestors beliefs.
Veiled |
- What esoteric practices
largely represent are humans who are curious about spiritual matters
and haven't foumd answers in traditional religion, or came from
different backgrounds than Jews and Christians.
- Also, members
of the enlightenment community in the 18th century believed the
ideas of esoterism failed to meet the standards of rationality that they deemed necessary for determining valid knowledge.

Talking bush |
- Unfortunately, not all esoteric practices are used for good
purposes and veer into black magic, use your discernment.
|
Not everyone believed that this cluster of ostensibly non-Christian traditions was compatible with Christianity. In the late 17th century, German Protestant polemicists denounced these traditions and cited their ongoing influence as evidence for the “paganism” infecting the Roman Catholic Church.
(brittanica.com)
|

Topics |
-
Alchemy,
Anthropospophy, Astrology, Freemasonry, Gnosticism, Greek Theogony, Hermeticism, Kabbalah,
Knights Templar, Martinism, Neoplatonism, Numerology, Paganism, Platonism, Reiki
Healing,
Rosicrucianism, Shamanism, Theosophy, Theurgy.
|
Alchemy |
Chemical science and speculative philosophy |
- At the core of Alchemy, is the desire to transform a substance of lesser value to something of greater value.
- Alchemic teachings originally focused on the transformation of
the self, the esoteric, and later concerned the exoteric, material compounds
in the physical
world.
- The purpose of Alchemy in early science was to transform base metals such as lead or copper into silver or gold, and to discover a cure for disease and a way of extending life.
|
Alchemy was the name given in Latin Europe in the 12th century to an aspect of thought that corresponds to astrology, which is apparently an older tradition. Both represent attempts to discover the relationship of man to the cosmos and to exploit that relationship to his benefit. The first of these objectives may be called scientific, the second technological.
(brittanica.com)
|
Hermes (Thoth) |
- According to Egyptian and Greek mythology, Hermes
(Thoth) was the founder of Alchemy after Thoth wrote the 42 books of
knowledge.
- Hermes Trismegistus was symbolized by the
Caduceus, balance, healing and protection, which represented
spiritual elevation and duality.
- Greek Hermeticism (Hermetism)
is a philosophical and religious system was also based on the
purported teachings of Hermes and involves Alchemy.

Transformation of
the self |
- There were different schools of Alchemy over the
centuries including Arabic, Hellenistic, Indian, Chinese, Greek,
European, Latin and what is called modern alchemy.
-
Despite the importance of Alchemy, very little written work has been
found; nothing has been found in India or ancient Middle America
(Aztecs, Mayans) and a single manuscript with 80,000 words is the
principal source from Greece.
- Chinese alchemy contains about
100 books that are included in the Taoist canon and no Islamic
alchemy has ever been collected.
|
Their secretive experiments, usually involving heat and the mixing of liquids, led to the development of pharmacology and the rise of modern chemistry.
(merriam-webster.com)
|
Transmutation |
-
Transmutation is
alchemical change in the state of being changed into another form;
such as radioactive decay or similar processes.
- Chinese ideas
about alchemy seem to go the furthest back in history and dealt more
with medicine and immortality.
|
Scholars have suggested that alchemy was never about creating gold but about the lessons learned along the way. Mixing metals to forge gold was never intended to be a realistic possibility. Instead, it was symbolic of the pursuit of knowledge and the futility of attaining material things like gold and wealth.
(Joe Duncan)
|
Elixir of
long life |
- Traditional Alchemy is based on three main objectives;
transformation of metals using the legendary Philosopher's stone,
the Elixir of Long Life to grant eternal youth, and spiritual
transformation which involves the elevation of the soul.
- The 'elixir of life' was first
mentioned in Europe about the 4th century BC also known as
'drinkable gold.'
- Evidence of the idea of transmuting base metals to gold appears
first in 2nd century AD Buddhist texts, about the same time as in the West.
|
Today we recognize alchemy as a pseudoscience, and give chemistry its rightful place as a serious scientific field, but the two terms initially overlapped in meaning before separating by the 17th century, just as astrology and astronomy did during the same period.
(merriam-webster.com)
|

Celestial bodies |
- Alchemy involves a series of stages where the Primordial
matter is mixed with sulfur and mercury, then heated in a furnace
passing through various stages of matter.
- Each of the 7
celestial bodies known to the ancients are represented with their
association with specific metals; Sun (gold), Moon (silver), Mercury
(mercury), Venus (copper), Mars (iron), Jupiter (tin), Saturn
(lead).
|
Anthropospophy |

Spiritual philosophy
|
- Anthroposophy is a belief that a human being passes
through stages of existence during the reincarnation of the human spirit.
- First we incarnate into an earthly body, then we live on Earth, leaving the body behind,
we then enter into the spiritual world before returning to be born again into a new life on
Earth.
- Anthroposophy is a spiritual religious movement which was founded in the early 20th century by the esotericist Rudolf Steiner.
- Steiner believed in balancing the spiritual and material aspects
of life and seeking harmony, as opposed to so many other doctrines
that devalue the role of the material world in balancing your life.
|
Anthroposophy has its roots in German idealism, Western and Eastern esoteric ideas, various religious traditions, and modern Theosophy.
(Wikipedia)
|
Christianity and
natural science |
- After 1900, Steiner worked with the Theosophical Society
and he received much attention from the group who supported his
ideas.
- However, by 1907 a split occurred because the
Theosophical Society was more concerned with Eastern and Indian
ideas, while Steiner was more interested in Christianity and natural
science.
- Steiner disagreed mainly with Theosophisist Annie
Besant when she compared Christ to the Eastern India Krishnamurti.
|
In contrast to mainstream Theosophy, Steiner sought to build a Western approach to spirituality based on the philosophical and mystical traditions of European culture.
(Wikipedia)
|
Perspectives on
self-knowledge |
- Steiner, who perfected his skills as spiritualist, was
one of the first to talk about the Akashic Records, which is a
chronicle of the history, pre-history, and future of the world.
-
In 1912, he formally broke with the Theosophical Society and formed
the Anthroposophical Society.
- Rudolf Steiner died in 1925.
|
The Second World War temporarily hindered the anthroposophical movement in most of Continental Europe, as the Anthroposophical Society and most of its practical counter-cultural applications were banned by the Nazi government. In reality, Steiner had both enemies and loyal supporters in the upper echelons of the Nazi regime.
(Wikipedia)
|
|
Astrology |

Cosmology and mysticism |
- Astrology originally came from Mesopotamia and later
incorporated into Greco-Roman antiquity.
- It
was founded on a set of beliefs in which the Sun, Moon, planets and stars have an
influence on each individual's destiny, personality and character traits.
- There are 12 signs of the zodiac in Western tropical astrology and
each has an opposing sign.
- They are divided into 4 elements: water, fire, wind and earth.
- Your birth sign is assigned when you are born, and is determined
by the position of the sun on the zodiac wheel and is your personal
timedatestamp.
|
Though often regarded as a science throughout its history, astrology is widely considered today to be diametrically opposed to the findings and theories of modern Western science.
(brittanica.com)
|
Astronomy |
- However, we are learning that all our 'science' appears
to be wrong because we've forgotten the esoteric knowledge and
spiritual meaning.
- Astronomy
is the science of studying the planets, stars and constellations in
the sky and is the foundation of astrology.
- It was used in
Mesopotamia to predict seasonal cycles and optimize harvests.
-
The Greeks added the concepts of the four elements (air, fire,
water, earth) and Arisotle called attention to the fifth element,
ether (Ophiuchus).
|
It is not in the stars to hold our destiny but in ourselves.
(Shakespeare)
|

Constellations |
- Astrology is not an exact science like astronomy but merely indicates trends and directions that can be altered either by divine or by human will.
-
It is also the practice of studying the movements and positions of celestial bodies.
- The Babylonians were aware of the 12 constellations and the 7
celestial beings and associated them with their gods and based on
their movements interpreted the messages given by the gods.
- Astrology has evolved into various branches including Hellenistic,
Indian and Chinese.
|
Zodiac signs “modify” the planets, adding nuance to their characters. The zodiac begins in the spring with Aries, which is the first sign, and travels through Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capircorn, Aquarius and finally to the last sign, Pisces.
(astrostyle.com)
|

Leo the Lion |
- The astrological signs are divided into two groups of
six; the first six are considered auspicious (good luck); Aries,
Gemini, Leo, Libra, Sagittarius and Aquarius.
- The last six are
considered unfavorable (bad luck); Taurus, Cancer, Virgo, Scorpio,
Capricorn, Pisces.
- All of us have all 12 signs in our zodiac,
some are more important, some less.
- In many cultures, there is
a belief that celestial bodies were living beings and capable of
influencing our lives on Earth.
Fire sign |
- Although astrology is not fortune-telling, when skillfully applied, astrology can be an effective predictive tool.
-
Some people seem overly concerned that astrology is no more
effective at predicting the future than just guessing, but that is
not the purpose of astrology.
- Instead you use it to figure out
what your strengths and weaknesses are, any predictions about the
future are based on patterns (like predicting snow in January).
|
In countries such as India, astrology manages to retain here and there its position among the sciences. Its continued legitimacy is demonstrated by the fact that some Indian universities offer advanced degrees in astrology.
(brittanica.com)
|
|
Freemasonry |

Mysticism secret societies |
- Freemasonry's long history includes its early development from organized bodies of stonemasons to the modern system of speculative lodges
centered around regional or national 'Grand Lodges.'
- The
formalization process of the order is generally taken to be the
creation of the first Grand Lodge in London in 1717.
|
Still to this day, the roots of modern Freemasonry are the subject of intense speculation, but the general consensus among Masonic scholars is that they lie with the medieval stonemasons that built our castles and cathedrals.
(ugle.org.uk)
|
Stonemasons |
- Guilds
were formed to help members gain employment and to uphold standards
of craftsmanship.
- Various skill levels were distinguished,
among other ways, through the use of secret handshakes and symbols.
|
In addition to learning the craft, members of the guilds also received esoteric knowledge, which in turn attracted non-craftsmen members to the guilds. These members became known as “non-operative” or “speculative” masons; gradually, with the decline in cathedral building, speculative masons took prominence in and eventual control of the organization. Drawing on the past, these individuals, who started to call themselves Freemasons, incorporated ritual and symbolic language, mostly relating to the building trades and specifically to the building of King Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem.
(encyclopedia.ushmm.org)
|

Big footed |
- The origins of Freemasonry are obscure and creation occurred over time between 1599 and 1721.
- The organization spread to America and played a role in the lives of many Founding Fathers.
-
Luciferianism belief system that the Architect of the Universe is
Lucifer and he will somehow save them.

George Washington |
- George Washington joined the Lodge in Fredericksburg, Virginia, in 1752,
and after his death, brothers of the Alexandria Lodge performed Masonic rites at his funeral.
- The president's last words were 'Tis well.'

Hand signals |
- In 1830, an attempt was made to steal the skull from the remains of American president George Washington, which resided in a tomb at Mount Vernon.
|
Everyone will sit under their own vine
and under their own fig tree,
and no one will make them afraid,
for the Lord Almighty has spoken.
(Micah 4:4)
|
Members |
-
Freemasonry began admitting Jews as members in the mid-18th century, first in England.

Landslide |
- The Secret Psychology of Freemasonry: Alchemy, Gnosis, and the Science of the Craft.
- Hammer Observing the Craft.
|
Gnosticism |
Pre-Christian |
- The word Gnosticism itself is derived from the Greek gnosis,
which means knowledge.
- At the core of all versions of Gnosticism is the idea that only through attaining secret
sacred knowledge can people find their salvation and overcome the material world.
- Gnostics focused on eradication of ignorance while Christians
believed they could eradicate sin.
Personal revelation
mirror |
- This knowledge is attained
through personal revelation rather than institutionalized, religious
doctrines and it places the individual's spiritual growth at the
heart of their relationship with the Divine.
- Alchemists, Freemasons, and Gnostics all fall under the branch of Hermeticism.
- Jesus himself was an Essene
Gnostic, one of the many sects which included Valentinianism, Sethianism and Mandaeism.
Eradication of
ignorance |
- Most popular Gnostic sects were heavily inspired by Zoroastrianism,
however, the origins are unknown and it seems to dwell on some
elements of Buddhism and early Jewish Christianity.
- Jesus was identified by some
Gnostics as an embodiment of the supreme being who became incarnate
to bring gnōsis to the Earth and as the male half of Sophia.
- Gnosticism had flavors of Mesopotamian, Syrian-Egyptian
and Persian.
- Samaritan Baptist sects were an offshoot of John the Baptist.
|
Gnostic writings flourished among certain Christian groups in the Mediterranean world around the second century, when the Fathers of the early Church denounced them as heresy. Efforts to destroy these texts proved largely successful, resulting in the survival of very little writing by Gnostic theologians.
(Wikipedia)
|
Sophia |
- In the Gnostic creation myth, Heaven, which the Gnostics called the
Pleroma (Fullness), was all that existed until a divine entity named Sophia tried to conceive on her own, without the involvement of her heavenly partner or the consent of God.
- As a result, Sophia fell to Earth and gave birth to a son that was the product of the rebellious and profane desire that had arisen within her,
and that was the Demiurge, who also represents government.
|
This son of hers was the demiurge. The Gnostic text Reality of the Rulers describes “him” as an androgynous being, an “arrogant beast” that resembled an aborted fetus in both appearance and character.
(gnosticismexplained.org)
|

Demiurge
born |
- The demiurge, 'craftsman,' is the being who the
Gnostics believed created the world and they identified him with the god of the Old Testament,
YHWH (Yahweh, Enki).
- Gnostic scriptures portray the demiurge, who represents the
lower ego, as ignorant, malicious, and utterly inferior to the true God who sent Christ to earth to save humankind from the demiurge’s evil
material world.
|
The demiurge is given many names in the Gnostic scriptures, but the three most common ones are Yaldabaoth (also spelled “Ialdabaoth”), Samael, and Saklas. “Saklas” comes from the Aramaic word for “fool,” and “Samael” is Aramaic for “Blind God” or “God of the Blind.
(gnosticismexplained.org)
|

Yaldabaoth |
- When Sophia saw the horrifying, twisted being that had come from her, she was deeply ashamed and afraid.
and she disowned him and cast him out of Heaven.
- The demiurge,
who was filled with madness and unchecked conceit, gave birth to the archons (rulers)
who were beings like him and could help him administer the material world.
- Yaldabaoth then created the material world, which, like all creations, was a reflection of the personality of its creator.
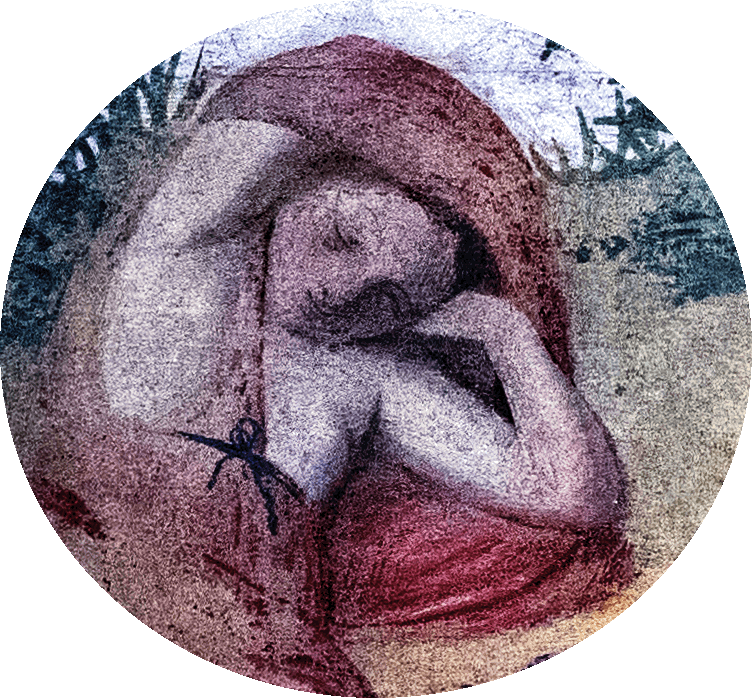
Eve clone |
- Next, the demiurge, Yaldaboath, created Adam and Eve
and he filled them with divine sparks from Heaven to light them.
- He created the 10 commandments and broke all of them himself,
including raping Eve.
- Yaldaboath, who wasn't the brightest
beam, did rape Eve but it was a clone of
her, she was smarter than him and already escaped.
- The Nag Hammadi texts place women in roles of leadership and heroism
- Gnostics took the
Biblical Genesis at its word and concluded that this god was simply malicious, hot-tempered, stupid, and inept.
|
He lied when he claimed to be the only god and that Adam and Eve would die if they ate the fruit of the Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil; he insulted his mother and father by refusing to acknowledge their existence; he made a graven image of the divine when he modeled the material world on his corrupt and ignorant misunderstanding of Heaven; and he committed adultery by attempting to rape Eve.
(gnosticismexplained.org)
|
|
Greek Theogony |

Cosmology and
Mythology |
- Greek theogony came about after the Greek pantheon,
which was established in the Homeric epoch, was further defined with
a geneaology and history and the result was Greek mythology.
-
The many entities that theogony defines can be found in the
Iliad and
the Odyssey.
- Hesiod's poem, The Theogony,
from 8th century BC, about the origin of the world, was the
earliest attempt at mythological classification.
- The Theogony
is the story of the history of the world from its creation, through the battle between the Olympians and the Titans, to the ascension of Zeus.
|
From the Heliconian Muses let me sing:
They dance on soft feet round the deep-blue spring
And shrine of Cronus’ mighty son upon
The great and holy mount of Helicon. (Hesiod, The Theogony)
|
Origin of the world |
- Hesiod wrote that in the beginning there was Chaos,
vast and dark, and then Gaia (Gaea), a deep-breasted Earth, and
finally Eros, 'the love which softens hearts.'
- From Chaos came
the night (Erebus) and day (Hemera).
- Gaia first bore Uranus,
the sky covered with stars, and she made him her equal in grandeur.
- Then she created the high mountains and the sea with
its harmonious waves.
Gaea mourned |
- Gaia united with her son, Uranus, and created the
first race, the Titans.
- Next they created the Cyclopes,
Brontes, Briareus and Gyges and Uranus regarded all his offspring
with horror and shut them up depths of the Earth.
- Gaea mourned,
and then became angered and tried to destroy Uranus through
meditation, bad thoughts.
- She crafted a sickle and enlisted her
son Cronus to kill Uranus.
- And that was the beginning of
everything.
|
Uranus fell to the ground, enraged and in terrible pain. The vicious attack upon him by his own son was realized too late. Swearing vengeance, he gathered what little strength he had left and disappeared, leaving Cronus alone to witness the monstrous forms at the gates of their prison, Tartarus.
(mythology.net)
|
|
Hermeticism |

Philosophy |
- Greek Hermeticism (Hermetism) is a philosophical and religious system based on the purported teachings of Hermes Trismegistus.
- Hermeticism, a mystical philosophy offers profound insights for personal transformation and spiritual enlightenment.
- The Egyptian Thoth (Djehuti or Zuhuti), who had the head of an
Ibis, was identified by the Greeks as Hermes Trismegitus (Mercury), messenger of the gods,
who was a moon god and patron of science and literature.
Natural harmony |
- In the
Hermetic tradition, hidden knowledge or spiritual wisdom is to be
discovered through meditation, contemplation, and the study of
sacred texts.
- Hermeticism differs from science in its aims as science seeks to study the natural world, Hermetics seeks to study the supernatural realm in hopes of gaining an understanding from that which isn’t readily apparent or intuitive.
-
The study of Hermeticism comes from Pythagoreanism, which is based on mystical teachings of natural harmony
and sacred geometry.
|
Pythagoras was obsessed with finding the secret fundamental substance of the cosmos, which is in line with the goals of all occultism. Alchemy grew out of this tradition.
(Joe Duncan)
|

The All is Mind; the
Universe is Mental |
- The Principle of Mentalism implies that the universe is mental, and everything that happens has a mental component.
- The Principle of Correspondence means that patterns repeat across different levels of reality;
as above, so below; as below, so above, as within, so without.
-
The Principle of Vibration implies that everything in the universe is in constant motion and vibration.
|
7 laws of hermeticism: Everything is dual; everything has poles; everything has its pair of opposites; like and unlike are the same; opposites are identical in nature, but different in degree; extremes meet; all truths are but half-truths; all paradoxes may be reconciled.
(Mastering the Gavel)
|

Differ in degrees |
-
The Principle of Polarity in Hermetic philosophy declares that opposites are identical in nature but differ in degree; it states that extremes meet and that all truths are but half-truths.
- The Principle of Rhythm revolves around the idea that there is a flow, a swing, a time for every purpose, which is observable in the natural world and all aspects of life.

Every cause has its effect |
- The Principle of Cause and Effect, another cornerstone of Hermetic philosophy, states that every cause has an effect, and every effect has a cause.
- The Principle of Gender, which speaks to the idea that everything contains both masculine and feminine principles.

Golden Dawn |
- Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn was a secret society devoted to the study and practice of occult Hermeticism and metaphysics during the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
- It was considered a magical order and was active in Great Britain
focusing its practices on theurgy and spiritual development.
-
The Golden Dawn system was based on hierarchy and initiation similar
to Freemasonry.
|
The foundational documents of the original Order of the Golden Dawn, known as the Cipher Manuscripts, are written in English using the Trithemius cipher. The manuscripts give the specific outlines of the Grade Rituals of the Order and prescribe a curriculum of graduated teachings that encompass the Hermetic Qabalah, astrology, occult tarot, geomancy, and alchemy.
(Wikipedia)
|
|
Kabbalah |
Jewish mysticism |
- Kabbalah (Kabalah, Cabala, Qabala) is Jewish mysticism or occult knowledge.
-
It is a part of Jewish tradition that deals with the essence of God
that centers on the belief that God moves in mysterious ways.
-
The Zohar is a Hebrew collection of written, mystical commentaries
about the Torah and is considered to be the
foundation of Kabbalah.

Red
self knot |
- The origins of the Kabbalah trace back to the Second Temple
period in Jerusalem in 6th century AD.
- However, its formal
roots began in the 12th century with the Kabbalistic texts
which explored themes such as creation and the nature of the divine.
- Kabbalah and Jewish mysticism, were traditionally not even taught to people until the age of 40, when they had completed their education in
Torah and Talmud.
- The mystical school of Jewish thought came to be known as Kabbalah, from the Hebrew root Qof-Beit-Lamed, meaning
'to receive, to accept.'
|
Kabbalah is the most famous form of Jewish mysticism. It flowered in 13th century Spain with the writing of the Zohar, which was originally attributed to the 2nd century sage Shimon bar Yohai.
(myjewishlearning.com)
|

Occult knowledge |
- The word Kabbalah is usually translated as
'tradition' and in Hebrew, the word does not have any of the dark, sinister, evil connotations that it has developed in English.
- Significant knowledge can be found in the Book of Light (Sefer
ha-Bahir) and the Book of Splendor (Sefer ha-Zohar).
- Kabbalah is based on a series of fundamental concepts; one example
is Gilgul, meaning souls can reincarnate in several lifetimes to
complete their journey.
- Kabbalah is not based on the 12
spheres of the Tree of Life and because it only has 10 spheres it's
Draconian and has been associated with black magic.
- This was
done to disconnect us from Christ consciousness because the spheres
relate to the 12 stargates and the 12th sphere is the connection.
One of 10 divine
emanations |
- Ein Sof (the infinity) is the ineffable aspect of God and is a
series of 10 divine emanations (Sephirot) manifest through which God
interacts with the world which are arranged as the Tree of Life and
used for meditation.
- A
common method is to meditate on the Hebrew alphabet which are
considered the basic units of reality through which God created the
world.
- Each letter is seen as a divine channel through which
Divine energy manifests in the world.
|
These misunderstandings stem largely from the fact that the teachings of Kabbalah have been so badly distorted by mystics and occultists. Kabbalah was popular among Christian intellectuals during the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, who reinterpreted its doctrines to fit into their Christian dogma.
(jewfaq.org)
|
Red string |
- Kabbala focused on the 10 emanations of God that had originally developed among the Jewish communities of France and Iberia in the 12th and 13th centuries.
- Wearing a thin scarlet or a crimson string as a type of talisman is a Jewish folk custom which is practiced as a way to ward off misfortune which is brought about by the
'evil eye.'
|
And it came to pass in the time of her travail, that, behold, twins were in her womb.
And it came to pass, when she travailed, that the one put out his hand: and the midwife took and bound upon his hand a scarlet thread, saying, This came out first.
And it came to pass, as he drew back his hand, that, behold, his brother came out: and she said, How hast thou broken forth? this breach be upon thee: therefore his name was called Pharez.
And afterward came out his brother, that had the scarlet thread upon his hand: and his name was called Zarah.
(Genesis 38:27-30)
|
|
Knights Templar |
Christian mysticism |
- The Knights Templar was originally called the Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon.
- They were founded 1119 AD
as a charity to defend
Christian pilgrims on their way to Jerusalem
following the First Crusade.
- Later, they became among the most legendary warriors in history, fighting against thousands in huge battles.
Military campaigns |
- They gained vast amounts of
military and financial power.
- Their headquarters were located in Jerusalem on the Temple
Mount for nearly two centuries during the Middle Ages.
- For nearly 200 years, the Knights Templar were at the center of politics and finance in Europe and took part in the Christian military campaigns in the Holy Land.
Dissolved |
-
After the Crusades ended, Muslim forces controlled Jerusalem, and military orders, including the Templars, were blamed for the loss of the Holy Land.
- This prompted demands to reform the military orders and many
called for them to be combined with other groups into a super order
to retake the Holy Land.
- In 1312, Pope Clement V officially dissolved the Knights Templar.
|
Philip IV of France, who was in financial debt to the Templars, ordered the mass arrest of French Templars on Oct. 13, 1307, confiscating their property and wealth.
(Livescience.com)
|
|
Martinism |

Mysticism and
metaphysics |
- Martinism is a form of Jewish-Christian mysticism and esoteric Christianity concerned with the fall of the first man, his materialistic state of being, deprived of his own, divine source, and the process of his eventual (if not inevitable) return, called 'Reintegration.'
- The essential principles of Martinism are much older than any organizations bearing that name.
- Martinism
was revived in France by Augustin Chaboseau and Gérard Encausse (Papus)
in 1884 when Papus drafted a constitution for the new Martinist Order.
|
Martinism A spiritual, mystical, and magical organization that has been derived and fused into the Martinist Order from the system of Martinez de Pasqually and the philosophy of Louis-Claude de Saint-Martin.
(occult-world.com)
|

Ethereal realms |
- In the 1890s the organization's Supreme Council was formed and
Papus became Grand Master.
- The goal was to return man to the divine source through spiritual enlightenment, which could be attained through the study of the laws of ethereal realms and communication with their spirits.
- It is a form of metaphysics and mysticism that was born in
Jewish-Christian freemasonry of 18th century France
|
Masonry is often called a secret society when we are
not. We are a public society that just happens to have
secrets. Martinism has some similar secrets in regards
to methods of recognition, but they go further in that
its members are in fact secret. One does not know who
all has been initiated into Martinism. That is
genuinely secret.
|

Spiritual
enlightenment, |
- By 1916, the order had 160 lodges in different countries,
including Russia.
- The Martinist Order degree teachings contain the mystical meanings of the great universal truths, Alchemy, thoughts, Numbers, the Kabbalah, and symbolic practices.
- There are different flavors of Martinism and some are related to Freemasonry.
|
Around the turn of the century, Papus made several visits to Russia, which, along with his contacts with Emperor Nicholas II, helped the rapid spread of Martinist ideas in the country.
(garagemca.org)
|
|
Neoplatonism |
Philosophy |
- Neoplatonism was a philosophical movement inaugurated
by Plotinus (204-270 BC), which reinterpreted the ideas of the
ancient Greek philosopher Plato.
- Plotinus' intent was to use Plato's thought as an intellectual basis for a rational and humane life.
- Neoplatonists believed that the individual soul, considered as intellect, is divine,
however, the soul is outwardly expressed in terms of a personality that is less divine.
- That presents the risk that a soul endowed with an intellect can lose sight of its own divine nature.
|
The Absolute "has its center everywhere but its circumference nowhere."
(Plotinus)
|

Divine spark |
- Neoplatonism developed as a school of thought in the Roman Empire from the
3rd to the 5th century.
- Where neoplatonism differs from Plato's
beliefs is that it seeks to locate the One, or God in Christian Neoplatonism, in the finite world and human experience.
- Iamblichus (250–330
AD) dominated a type of Neoplatonism that came to dominate the Platonic schools in the 5th and 6th centuries.
|
This later Neoplatonism aspired to be not only a complete and coherent metaphysical system but also a complete pagan theology. (britannica.com)
|
|
Numerology |
Egyptians |
- The Egyptians and Babylonians were among the first to
recognize the importance of numbers in their religious and
scientific practices.
- Pythagoras is considered the father of
numerology as we know it today.
- In the Middle Ages, numerology
was integrated into Kabbalah and Alchemical traditions.
- Each
number has a particular meaning in numerology such as 1 (inception
and leadership), 2 (harmony and collaboration), etc.

Numerology systems |
- The most
common numerology system is the Pythagorean method where each letter
of the alphabet is associated with a number.
- There are other
systems or interpreting numbers such as the Chaldean method (simple
gematria) which is from Mesopotamia and is the method of assigning
letters to numbers 1-8.
Gematria |
- Gematria, which has a Hebrew origin, is the practice of assigning a numerical value to a name, word or phrase by reading it as a number, or sometimes by using an alphanumerical cipher.
- It involves reading words and sentences as numbers, assigning
numerical instead of phonetic value to each letter of the Hebrew
alphabet (although it is used for other languages).
|
You can search your name or any other phrase and the online gematria calculator will calculate the Gimatria value not only in English but also in Hebrew Gematria, Jewish Gematria and the Simple Gematria method.
(gematrix.org)
|
Personality code |
- There are different types of codes that can be generated using
numerology, such as the personality code.
- First you perform a
theosophical reduction on your full name (calculate the value of
each letter and add them together and reduce to a single digit).
- Each reduced number is associated with values such as creativity,
optimism; words that define a person at their core.
Sacred geometry |
-
Sacred geometry
encompasses all the shapes and patterns in nature.
- In its simplest definition, sacred geometry is the meaning and symbolism that is attributed to certain shapes and proportions.
- On a spiritual level, and according to many ancient traditions,
everything in the cosmos arises from sacred geometry.
-
According to Pythagoras, numbers govern the Universe.
Golden Mean floats |
- The Golden Mean (phi or the Golden Ratio), is a mathematical law that represents Infinity
and proves everything has the ability to divide and subdivide.
- According to the Golden Mean, every part relates to another part and can continue to divide and subdivide for eternity.
- Platonic Solids are the sacred shapes tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron.
- The Platonic Solids are named after the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, who said each of these shapes corresponds with one of the elements: earth, fire, air, water, and ether.
|
Paganism |
Ethnic religion |
- Paganism concerns religious beliefs other than those of the main or recognized religions.
- During and after the Middle Ages, the term paganism was applied to
any non-Christian religion, and the term presumed a belief in 'false
gods.'
- Paganism is a Christian term used to designate those religions that do not worship the God of Abraham, the figure central to both Christianity and to other Abrahamic religions like Judaism and Islam.
|
The 15th to 19th centuries saw Christian Europeans expand into new areas across the Americas, Asia, Africa, and Australasia. In these lands they encountered a huge variety of religious traditions not devoted to the God of Abraham and which again they often labeled pagan or heathen.
(brittanica.com)
|
Druidry |
- Druids took thwir identity from the Iron Age ritual specialists of Western Europe, and Heathenry,
some spent as much as 20 years in training.
- The principal source of information about the Druids was Julius
Caesar who claimed that the Druids took charge of public and private sacrifices, and
that many young men went to them for instruction.

Druid religious
leader |
- The Druids beliefs were modeled on the pre-Christian religions of
cultures that spoke Germanic languages like Old Norse.
- Druids studied ancient verse, natural philosophy, astronomy, and
mythology of the gods.
- They were said to believe that the soul was immortal and passed at death from one person into another.
|
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts.
(Wikipedia)
|

Wicca
Samhain |
- New religions, such as Wicca, that venerated the same
pre-Christians traditions as early pagans, began emerging in the
1960s.
- Wiccans consider Samhain as the passing of the year, and incorporate common Wiccan traditions into the celebration.
- They celebrate the cyclical nature of life and the sacredness of
gods, goddesses, and the Great Mother (virgin, mother, elder) who
was venerated as a triple goddess and a solar god.
- Wiccans core
beliefs were the celebration of lunar and solar cycles, respecting
nature, and observing the law of three-fold return.
|
It then draws near the season Wherein the spirit held his wont to walk.
(Shakespeare, Hamlet)
|
Lunar and solar
cycles |
- There are many forms of Wicca with the earliest, Garneriana
(1950), which is about altars, sacred spaces, magic and spells,
working with energy, Sabbaths and Esbat, initiations and circle
rituals.
- Alexandrian Wicca (1960) focuses more on ceremonial
magic and Eclectic Wicca deals with occultism, Golden Dawn,
witchcraft, Hermeticism and Hoodoo.
- Collectively,
newer groups came to be called Neo-Pagan or modern Pagan, a deliberate
use of the biased Christian term.
|
Platonism |
Philosophy |
- Platonism is the philosophy of Plato (428-347 BC), and philosophical
systems closely derived from it that had a profound effect on Western thought.
- Plato's influence spread because he wrote about a
wide array of topics with a methodological reasoning that was not
necessarily religious or spiritual.
- He practiced a rational,
organized approach to thinking.
- The origin of Platonic philosophy
began with Ancient Egypt or because of ancient knowledge called the
'Chaldaic mysteries,' which represented the occult 'Eastern wisdom.'
- Platonism was the dominant philosophical position in the ancient world
for more than 800 years.
|
The object of Art is to give life a shape.
(Shakespeare, Hamlet)
|
Abstract objects
like triangles |
- The main theory of Platonism is that numbers or other abstract objects are objective, timeless entities, independent of the physical world and of the symbols used to represent them.
- Their theories are based on a belief in unchanging and eternal realities (the Platonic forms), independent of the changing things of the physical world perceived by the senses.
|
The existence of abstract objects represents a significant challenge for the Christian in particular and for Traditional Theists in general since it is central to these worldviews that God is the creator of everything other than God himself. Generally, however, abstract objects are considered to be like God in that they are said to have always existed, and to always exist in future. Consequently, there is no point at which God is considered to have brought them into being.
(iep.utm.edu/pla-thei)
|
Quality of human
life |
-
Platonism is concerned about the elevated status of the human soul
as well as the quality of human life and ethics,
and they sometimes concern themselves with religion and politics.
- There are different versions such as Cambridge Platonism
which was a 17th-century attempt to reconcile Christianity with humanism and science.
|
Platonism has had some influence on Christianity through Clement of Alexandria and Origen, and the Cappadocian Fathers. St. Augustine was heavily influenced by Platonism as well, which he encountered through the Latin translations of Marius Victorinus of the works of Porphyry and/or Plotinus.
(Wikipedia)
|

Platonic forms |
- Platonism has never accepted incarnation and the resurrection of the body
and therefore, clashes with Christianity.
- The three main
periods of Platonism are called Old Academy, Middle Platonism, and New Academy.
- Plato’s concept of God was of one who formed out of chaos, rather than out of nothing,
and he believed that the body and soul were completely separate, such that the body was inferior to the soul.
- Plato believed that moral behavior was always a matter of education.
|
Among the most important of these abstract objects (as they are now called, because they are not located in space or time) are goodness, beauty, equality, bigness, likeness, unity, being, sameness, difference, change, and changelessness.
(Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
|
|
Reiki Healing |
Energy centers |
- Reiki involves laying hands on key energy centers within the body, basically along the same lines as chakra balancing and healing.
- The technique originated in Japan in the early 20th century.
- Reiki is a combination of two Japanese words:
'rei,' which means 'God’s wisdom,' or 'the higher power,' and 'ki,'
which means 'life force energy.'
-
Reiki is a technique that uses energy force to reduce stress and anxiety and encourage relaxation.
- It’s not a religion and is not associated with religious practice.
|
Reiki may not be able to cure illness on its own, but it can offer profound relief from chronic fatigue, pain, anxiety, and depression. It’s become more popular in hospitals as a complement to Western medicine, as studies have shown that it helps to promote peace and relaxation in patients undergoing surgery.
(theholisticcounseling.center)
|
|
Rosicrucianism |

Jewish mysticism and
Christian gnosticism |
- Rosicrucian teachings are a combination of occultism and other religious beliefs and practices, including Hermeticism, Jewish mysticism, and Christian gnosticism.
-
It's a 17th and 18th century movement professing esoteric and occult wisdom with emphasis on mysticism and spiritual enlightenment.
-The main belief of Rosicrucianism is that its members possess secret wisdom that was handed down to them from ancient times.
|
The outer and inner Mind
Without God's light you cannot find.
|

Secrets about
medicine and magic |
- The earliest authentically Rosicrucianism writings come from the 17th century anonymous works
that identified the alleged founder of the order as Christian Rosenkreutz.
- Rosenkreutz learned secrets about medicine and magic while on a trip to the Near East
and when he returned to Europe, he founded a secret fraternity whose members communicated in secret-coded writings.
- The Rosicrucianism Order is syncretistic
because it borrows ideas and beliefs from various other religions in an
attempt to unify them under a central theme.
|
Wisdom about life after death has been preserved through the ages and is revealed only to the secret brotherhood.
(gotquestions.org)
|
Rosy wood |
- Rosicrucianism is symbolized by the Rosy Cross or Rose Cross.
- Rosicrucianism rejects the divine authorship of the Bible and does not hold Scripture in any special favor.
-
They believe that Jesus Christ was born of Gentile parents, did not die on the cross, did not ascend to heaven, and retired to the monastery in Carmel to carry on secret missions with His apostles.
- The combination of alchemy and mysticism associated with
Rosicrucianism became quite influential.

ESP, clairvoyance
and spiritism |
- Some of the occultic teachings in Rosicrucianism include ESP, clairvoyance and spiritism.
- The practice was attractive to many thinkers throughout Europe, possibly including the English philosopher and scientist Francis Bacon.
- Popularity declined dramatically in the 18th century because of skepticism and rationality.
|
Within this world three Worlds in each other, namely this earth Sun-World, and also the Heavenly and the Hellish world have their effects. And the darkness cannot conquer the light. It also shows that the land of the dead, the entrance to Hell or superficial darkness, where there is wailing and gnashing of teeth, as well as the land of the living, the heavenly paradise or third heaven are from this world. And that the human being has all these things in his heart; heaven and hell, light and darkness, life and death.
(The Teachings of the Rosicrucians)
|
|
Shamanism |

Ecstatic religious
experience |
- Shamanism is a religious phenomenon centered on the shaman, a person believed to achieve various powers through trance or ecstatic religious experience.
-
Shamans, 'one who knows' are found in many cultures and are known
for their ability to heal the sick, communicate with the dead, and often to escort the souls of the dead to the otherworld.
-
Shamanism generally describes indigenous groups in which roles such as healer, religious leader, and counselor are combined.
|
The origins of Shamanism stem from indigenous peoples of far northern Europe and Siberia.
(Wikipedia)
|

Shaman Elephant |
- Shamanic traditions around the world use the archetypes of power animals as allies, advisors, and protectors on our life's journey.
-
They believe that everyone has power animals, animal spirits that reside within each individual adding to their power and protecting them from illness.
-
Shamans are born into the role and trained by spirits.
Angel fish |
- The Shaman may fulfill his obligations either by communicating with the spirits at will or through trance.
- Shaministic groups aroumd the world have differing practices,
for example, the Siberians employ drums and astral journeys using
trance rituals, while Africans focus on complex rituals with
talismans and spells often for community healing and protection.
|
The extraordinary profession of the shaman
naturally distinguishes him socially. The belief that
he communicates with the spirits gives him authority.
Furthermore, the belief that his actions may not only
bring benefit but also harm makes him feared. Even a
good shaman may do inadvertent harm, and a wicked
shaman, who is in contact with the spirits of the
Lower World, is very alarming.
(britannica.com)
|

Shaman power animals |
- At the core, Shamanism is the practice of connecting with the
unseen realms to connect with spirits (ancestors), and communicating
with the natural world.
- They use methods such as prayer,
drumming and sometimes psychedelic substances that act as a link
between the spiritual and physical worlds by reaching different
stages of consciousness.
- Shamanism has been regarded as one of the world’s oldest religions.
|
Tarot Cards |

Mysticism |
-
Tarot, any of a set of cards used in tarot games and in fortune-telling
and it began with simple playing cards.
- There are a lot of esoteric theologies and doctrines that go into Tarot, from Kabbalah to Astrology.
- With the rise in occultism im the 14th century in Italy, Eliphas
Levi, cotributed to codifying Tarot's symbolism, associating the
symbols with Alchemy and Kabbalah.
- Levi associated Tarot with
arcane wisdom which is esoteric and mysterious knowledge reserved
for a few.
- The Tarot reader should always test the spirits before every
reading.
|
All difficulties are easy when they are known.
(Shakespeare)
|
Major arcana |
- The standard tarot deck is based on the Venetian or the Piedmontese tarot
and consists of 78 cards divided into two groups: the major arcana, which has 22 cards, also known as trumps, and the minor arcana, which has 56 cards.
|
Tarot decks were invented in Italy in the 1430s by adding to the existing four-suited pack a fifth suit of 21 specially illustrated cards called trionfi (“triumphs”) and an odd card called il matto (“the fool”). (The fool is not the origin of the modern joker, which was invented in the late 19th century as an unsuited jack in the game of euchre.) (britannica.com)
|

Angelic spirit guide |
- The adaptation of Tarots to occult and divination purposes
called an oracle first occurred in France about 1780.
- The cards of the major arcana refer to
major universal themes such as spiritual matters and important trends in the questioner’s life.
- In the minor arcana 'wands' deal mainly with business and career,
'cups' with love, 'swords' with conflict, and 'coins' with money and material comfort.
|
Are not all angels ministering spirits sent to serve those who will inherit salvation. (Hebrews 1:14)
|
Spread |
- Cards are laid out by a Tarot reader in a special pattern called a
'spread.'
- The interpretation of any card is determined by the
interaction between cards rather than the individual meanings of the
cards.
- This includes things like whether the card is upside down, its position in the spread, and the meaning of adjacent cards.
- There are many types of spreads
including an eleven-card layout called the Celtic Cross (11 cards including the Significator).
- There is also a Tree of Life spread, a Planetary spread, the Tetraktys spread, and the Pentagram spread, among many others.
|
Tarot reading is the practice of divining wisdom and guidance through a specific spread (or layout) of Tarot cards. However, contrary to popular belief, the cards do not simply tell your fortune, and one does not have to be a psychic to give Tarot readings. The cards are meant to provide insight into the innermost truths of your higher self. (sagegoddess.com)
|
|
Theosophy |
Mysticism |
-
The contemporary movement began with the founding of the Theosophical Society in New York City in 1875 by Helena Petrovna Blavatsky (1831–1891), Henry Steel Olcott (1832–1907), and William Quan Judge (1851–1896).
-
Theosophy is the teaching about God and the world based on mystical insight
and spiritual evolution based on cosmic laws.
- The teachings of the movement chiefly followed Buddhist and Brahmanic theories especially of pantheistic
evolution and reincarnation and its roots can be traced to ancient Gnosticism and Neoplatonism.
- Theosophists sacred text is the Book of Dyza which
Blavatsky described as an ancient Tibetian manuscript dating to
prehistoric eras.

Eastern thought in
the West |
- The term theosophy, derived from the Greek theos (god) and sophia (wisdom), is generally understood to mean
'divine wisdom.'
- Theosophists pioneered the promotion of Eastern thought in the West and also inspired the creation of more than 100 esoteric religious movements.
- Theosophy displays a preference for monism, the view that reality is constituted of one principle or substance, such as mind or spirit.
- Luciferianism belief system (outgrowth is Lucas Trust and the
UN).

Ancient secrets |
- Blavatsky traveled to Tibet and learned ancient secrets from
the Great White Brotherhood who transmitted the occult arts.
- The most
notable Master she studied under was Morya, who was the leader of the
Great White Brotherhood.

Deeper spiritual
reality |
-
Theosophy teaches about a deeper spiritual reality and how direct contact with that reality can be established through intuition, meditation, revelation, or some other state,
thereby transcending normal human consciousness.
-
Interest in the supernatural or other extraordinary occurrences and with the achievement of higher psychic and spiritual powers.
-
They believed that God was trnscendent and impersonal, that creation is the product of spiritual emanations from God, and that humans are sparks of the divine trapped in the material world who desire to return to their spiritual home.
|
Theosophists also emphasize esoteric doctrine. Modern theosophists claim that all world religions contain such an inner teaching, and much attention is devoted to deciphering the meaning concealed in sacred texts.
(brittanica.com)
|

Spiritual evolution |
- Theosophists believe that the world evolves through a
series of intermediate stages between matter and spirit, reflecting
a process of gradual refinement.
- This is the transistion from
primordial matter (prakriti), to physical body, to etheric body, to astral body, to soul
and ending in spirit.
- There is no beginning
or end and the human soul is destined for a continuous cycle of
reincarnation, birth and death (infinity), until the soul reaches the pure
essense of the cosmos.
- This is accompanied by a process of
karma, good and bad, where actions in one life influence destiny and subsequent
incarnations.
|
Theurgy |

Supernatural |
- Theurgy (Theoi-urge),
god's work or activity, was a belief from Iamblichus of Syria (240–325 AD), whose teachings set the final form of pagan spirituality prior to the Christianization of the Roman Empire.
- It is a ritualized form of closeness with the divine for salvific purposes
which used ritual prayer and offering, and devotional activity
coupled with meditation, to bring the gods activity into the cosmos.
- Theurgy which means 'divine action,' is the the operation or effect of a supernatural or divine agency in human affairs.

Divine power |
- The art or technique of compelling or persuading a god or beneficent or supernatural power to do or refrain from doing something.
- Theurgic rituals in late antiquity went usually in stages and were heavily influenced by Egyptian religion.
- To the layman, it is considered magic.
- English author and occultist Aleister Crowley (1875–1947) wrote about magical practices and theory, including those of theurgy ('high magic') and goetia ('low magic').
- Also involves systematic ritual practices using hymns, talismans, and sacred objects.
|
The object is to honor the divine or the One according to Neoplatonic cosmology. This involves what's called The One, which created the Nous (mind, intellect, divine consciousness), which created the Soul, which created the material realm humans inhabit. Getting closer to divinity is achieved through theurgical acts.
|
Prayers, divination
and rituals |
- It was a series of prayers, divination and rituals used to
perceive their gods using lecanomancy (water bowl divination) or
lychnomacy (lamp divination).
- This was called autoptos, or perceiving god face to face,
and systasis, arrival of the god.
- This can include the
entering of divine power (dynamis) into the theurgist and
immortality.
- Elus Cohens (Coëns), a type of 'Martinist' focused on theurgy
and the aim of his order was magical in nature, however, it died out in the 18th
century.
|
Sweets to the sweet.
(Shakespeare)
|
The truth of things is the chief nutriment of superior intellects.
Leonardo DaVinci

| |
 |
 |

